In this article, we will explore Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), its definition, construction, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. So, let’s begin with the basic definition of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT).
What is Bipolar Junction Transistor?
A Bipolar Junction
Transistor, also known as BJT,
is a semiconductor electronic device having three semiconductor regions and is
used as an amplifier or solid-state switching in different electronic circuits.
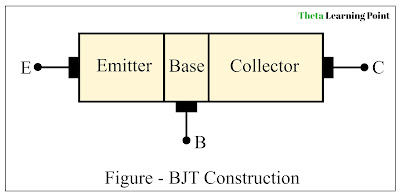
The construction of bipolar junction transistors consists of three layers of semiconductor material namely, emitter, base, and collector as depicted in the above figure. Three metallic conductors are attached to these three semiconductor layers to form terminals of the bipolar junction transistor. Therefore, BJT has three terminals namely, emitter (E), base (B), and collector (C).
A BJT typically has two pn-junctions namely, emitter-base
junction and collector-base junction. Thus, BJT is a three-layer,
three-terminal, and two-pn-junction device.
In the BJT, the emitter is the heavily doped region, the
base is the lightly doped region, and the collector is the moderately doped
region. In terms of physical size, the collector is the largest, the base is the smallest, and the emitter is medium.
Types of Bipolar Junction Transistors
Based on the construction, Bipolar Junction Transistors
(BJTs) are primarily classified into the following two types:
- NPN Transistor
- PNP Transistor
Now, let us get a brief overview of NPN and PNP transistors
individually.
NPN Transistor:
NPN transistor is a type of BJT that is constructed by
sandwiching a p-type semiconductor between two layers of an n-type semiconductor.
Therefore, the NPN transistor has an N-type emitter region, P-type base region, and
N-type collector region. The construction diagram of the NPN transistor
is depicted in the following figure.
PNP Transistor:
PNP transistor is constructed by sandwiching a layer of
n-type semiconductor between two layers of p-type semiconductor. Thus, in the
case of a PNP transistor, the emitter is of p-type, the base is of n-type, and
the collector is of p-type. The construction diagram of the PNP
transistor is shown in the following figure.
Advantages of Bipolar Junction Transistor
Bipolar junction transistor (BJT) has several advantages. Some
key advantages of BJT are given below:
- Bipolar junction transistors have the ability to handle high currents and power levels.
- Bipolar junction transistors have higher voltage gain.
- Bipolar junction transistors have larger gain bandwidth.
- The forward voltage of bipolar junction transistors is low.
- Bipolar junction transistors have high current density.
- Bipolar junction transistors provide better performance at high frequencies.
- Bipolar junction transistors can be efficiently used in a wide range of applications from low to high power levels.
- Bipolar junction transistors are typically more robust.
- Bipolar junction transistors are less expensive and simpler to design.
Disadvantages of Bipolar Junction Transistor
Bipolar junction transistors also have some limitations. Some
major disadvantages of BJTs are listed below:
- Bipolar junction transistors have lower input impedance.
- Bipolar junction transistors have lower thermal stability that can impact the performance of the circuit.
- Bipolar junction transistors produce more noise that affects overall system performance.
- Bipolar junction transistors consume relatively more power which reduces the efficiency of the circuit.
- Bipolar junction transistors have comparatively larger physical sizes.
- Bipolar junction transistors require a complex control circuit.
- Bipolar junction transistors have low switching frequency.
Applications of Bipolar Junction Transistor
The following are some important applications of bipolar junction
transistors (BJTs):
- BJTs are used in digital logic circuits.
- Bipolar junction transistors are employed for the amplification of analog signals in a variety of electronic systems, such as audio systems, communication systems, radio frequency amplifiers, etc.
- Bipolar junction transistors can also be used as a static switch in electronic circuits.
- Bipolar junction transistors are used in oscillator circuits to produce waveforms of different frequencies.
- Bipolar junction transistors are also used in voltage regulators to stabilize the load voltage.
- Bipolar junction transistors are used in motor driver circuits.
- BJTs are also used in power supplies.
- BJTs are also used in timer circuits.
Hence, this is all about Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs), their construction, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.



.png)



0 Comments