Introduction to Multimeter
A multimeter is a multi-purpose device used in electrical
and electronic practices to measure different electrical quantities like
current, voltage, resistance, etc. in an electric circuit.
Since, it combines the functions of a voltmeter, ohmmeter, and
voltmeter in a single unit. Therefore, it is also known as a volt-ohm-amp meter.
Today, multimeters have a wide range of applications in
various fields, including electrical, electronics, instrumentation, IT and
hardware, and more. The greatest benefit of a multimeter is that it allows all
the necessary measurements required for troubleshooting faults by using a
single device. Another major advantage of a multimeter is that it has a compact
design, making it easy to carry from one place to another.
Types of Multimeter
Multimeters can be classified into the following two major
types depending on their construction and working principle:
- Analog Multimeter
- Digital Multimeter
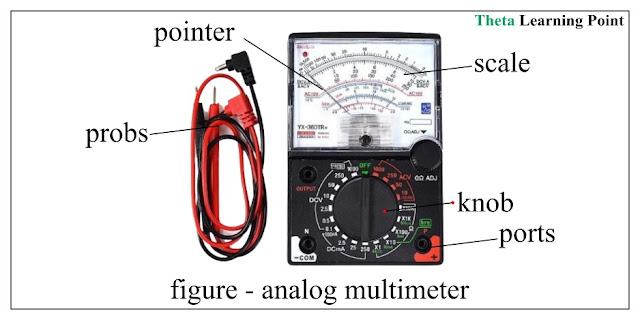
(1). Analog Multimeter:
Analog multimeter is an older version of the multimeter. It
is designed by using a permanent magnet, a moving coil, a pointer, and a
calibrated analog scale.
An analog multimeter displays readings through the
deflection of a pointer on a calibrated scale. The advantages of analog
multimeters include low cost, continuous reading, a wide range of measurements,
etc. However, these are less accurate, confusing to use due to multiple scales,
and larger and bulky.
(2). Digital Multimeter:
A digital multimeter, also known as DMM, is a modern version
of the multimeter. It utilizes semiconductor components and a digital display to
show the readings. A standard digital multimeter can perform all the basic
measurements like current, voltage resistance, transistors gains, continuity,
etc. Although, there are several advanced digital multimeters also available to
perform complex measurements.
The major advantages of a digital multimeter include lightweight and compact design, auto-polarity, auto-range selection, affordable, and
ease to use.
Functions of a Multimeter
The functions performed by a multimeter depend on its type
and the model. A basic multimeter can perform measurements of current, voltage,
resistance, transistor gain, and continuity.
A list of functions that multimeters can perform is given
below:
- Resistance measurement
- Current measurement
- Voltage measurement
- Capacitance measurement
- Inductance measurement
- Temperature measurement
- Frequency measurement
- Transistor testing
Advantages of Multimeters
The benefits of using multimeters in electrical and
electronic measurements are as follows:
- Versatility – A multimeter is a versatile instrument that allows for the measurement of various quantities like current, voltage, resistance, etc. using a single device.
- Portability – A multimeter combines functions of various measuring instruments like an ammeter, voltmeter, ohmmeter, etc. in a small-sized and lightweight box unit. This makes it portable and easy to carry from one place to another.
- Efficiency – The use of multimeters in electrical practices simplifies the measurement and reduces the troubleshooting time. This results in improved efficiency.
- Accuracy – Multimeters allow for accurate measurement of electrical quantities.
Disadvantages of Multimeters
A list of key disadvantages of multimeters is given below:
- Multimeters are mainly designed for general-purpose measurement applications. Thus, they have limited accuracy in the case of highly specialized measurement applications.
- Multimeters cannot provide a depth analysis of measurement in some complex electrical phenomena.
- Multimeters are typically designed to perform steady-state measurements. Thus, they may not be capable to perform measurements of transient events.
- Some models of multimeters are complex to use for beginners.
Applications of Multimeters
The following are some key applications of multimeters:
- Multimeters are used to test faulty circuits and appliances.
- Multimeters are used to test cables for their continuity.
- Multimeters are also used to test semiconductor devices, like diodes, transistors, etc.
- Multimeters are widely used in various industrial applications, such as for the measurement of current, voltage, resistance, temperature, frequency, and many other circuit parameters.
- Multimeters are also used in automobiles to test their battery, alternator, horn, and other electrical and electronic components and circuits.
Hence, this is all about a multimeter and its applications.
In conclusion, a multimeter is a versatile instrument, that allows one to perform all
the basic measurements using a single device.



.png)





0 Comments